Topics
late
AI
Amazon
Image Credits:Felice Frankel/MIT
Apps
Biotech & Health
mood
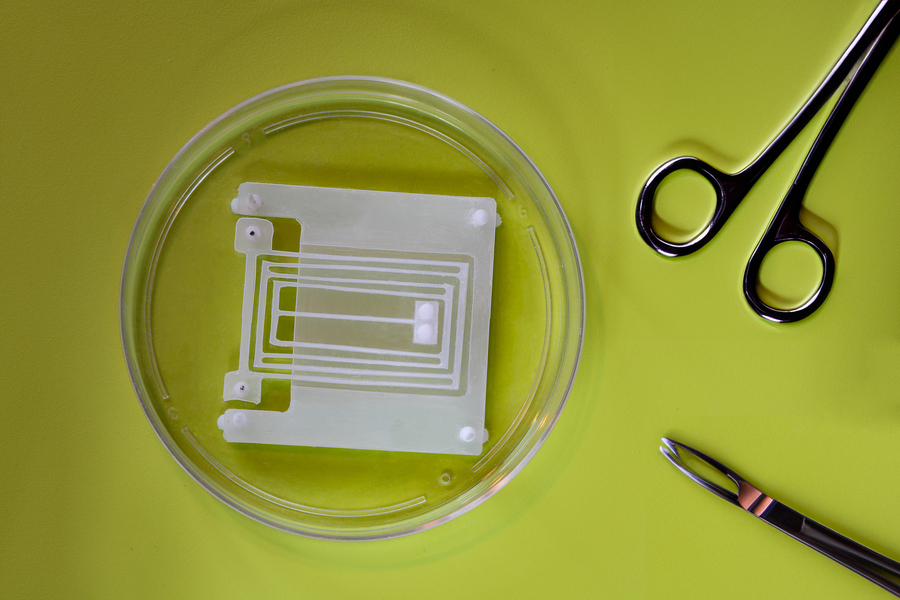
Image Credits:Felice Frankel/MIT
Cloud Computing
Commerce
Crypto
initiative
EVs
Fintech
fundraise
Gadgets
game
Government & Policy
Hardware
Layoffs
Media & Entertainment
Meta
Microsoft
Privacy
Robotics
Security
societal
Space
Startups
TikTok
Transportation
Venture
More from TechCrunch
effect
Startup Battlefield
StrictlyVC
Podcasts
Videos
Partner Content
TechCrunch Brand Studio
Crunchboard
Contact Us
Sometimes nature provides the secure blueprints for building effective robots . It also can cater the best material . billion of old age of natural excerption has build some fairly impressive machinery , so you ca n’t really blame engineers for borrow a minute of brainchild from the world around them . In fussy , the field of soft robotics — with its pliant and compliant components — owe a lot to animal biology .
While these system have balmy forms , however , many of their component are still rigid like their more traditional counterparts . Researchers are work to fetch flexible element to make motivity for these soft robots . As MIT succinctly order it , “ our muscles are nature ’s perfect actuators . ”
The team is going beyond simply mimicking brawn here , however . Researchers at the schoolare usinglive sinew tissue in tandem with semisynthetic robot parts for a classification of robots roll in the hay as “ biohybrid . ”
MIT Professor of Engineering Ritu Raman confirmed the mental process with TechCrunch , take note , “ We build the muscle tissues from mouse cells , and then we put the muscleman tissues on our automaton ’s skeleton . The muscles then go as actuator for the golem — every time the muscle contract , the automaton moves . ”
The muscle roughage are attached to a “ natural spring - corresponding ” gimmick called a “ flexure , ” which serves as a variety of skeletal social organization for the system . Biological muscle tissue can be hard to work with and mostly unpredictable . Left in a Petri dish , the tissue will expatiate and contract as hoped for , but not in a controlled manner .
In ordering to be deployed in robotlike systems , they have to be reliable , predictable and repeatable . In this instance , that requires the manipulation of structures that are compliant in one focus and immune in the other . Raman ’s squad find a solution in Professor Martin Culpepper ’s MIT prevarication lab .
The fold still need to be pluck to the specifications of the robot , at last opting for structure with 1/100ththe clumsiness of the muscle tissue . “ When the muscle sign up , all the force is exchange into movement in that way , ” Ramannotes . It ’s a Brobdingnagian magnification . ”
Join us at TechCrunch Sessions: AI
Exhibit at TechCrunch Sessions: AI
The muscle fiber / crease system can be apply to various variety of golem in different sizing , but Raman say the team is focused on creating extremely lowly robots that could one day work inside the dead body to perform minimally invasive procedures .